What Is GLP-1?
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1(GLP-1), is a hormone produced in the intestines that plays a key role in glucose metabolism and appetite regulation. It is one of several incretin hormones, which means it helps stimulate insulin secretion in response to food intake. An effects make it particularly important in managing blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss.
a) How GLP-1 Is Released
GLP-1 is secreted by the L-cells in the small intestine when we eat. It is released into the bloodstream, where it travels to various parts of the body, including the pancreas, stomach, and brain. Upon release, it has several actions that help regulate blood sugar and control appetite.
b) Functions
GLP-1 primary functions:
- Stimulating Insulin Secretion: enhances the secretion of insulin from the pancreas in response to elevated blood sugar levels, which helps lower blood glucose.
- Suppressing Glucagon: reduces the secretion of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels, thereby preventing post-meal spikes.
- Slowing Gastric Emptying: It slows down the emptying of the stomach, making you feel full longer and reducing overall food intake.
- Promoting Satiety: interacts with receptors in the brain to promote feelings of fullness, helping with weight management.
For a more detailed look, visit Zappy Health’s blog medications.
The Role of GLP-1 in Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. It plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes by improving glucose control.
a) Insulin Sensitivity
It helps the body become more sensitive to insulin by encouraging the pancreas to release more insulin when blood sugar levels are high. This action is particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes, who often struggle with insulin resistance.
b) Benefits for Blood Sugar Control
GLP-1’s ability to suppress glucagon and slow gastric emptying further helps keep blood sugar levels stable after meals, preventing the postprandial blood sugar spikes that can be harmful over time.
c) A Breakthrough in Diabetes Treatment
Pharmaceutical companies have developed GLP-1 receptor agonists, a class of medications that mimic the action of natural GLP-1. These drugs help manage blood sugar levels more effectively in people with type 2 diabetes.
Common receptor agonists include:
- Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy)
- Liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda)
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
These medications have shown significant benefits in reducing HbA1c levels, a key marker of long-term blood sugar control.
For more information on GLP-1 agonists and their role in diabetes management, see Zappy Health’s guide.
GLP-1 and Weight Loss
In addition to managing diabetes, GLP-1 has gained attention for its weight loss benefits. The hormone’s ability to slow gastric emptying and reduce appetite makes it a valuable tool for weight management, especially in individuals with obesity or overweight conditions.
a) Appetite
GLP-1 acts on the appetite centers in the brain, particularly the hypothalamus, to promote feelings of fullness. By reducing hunger, people taking this receptor agonists often consume fewer calories, leading to weight loss.
b) Approved for Weight Loss
While many GLP-1 agonists are used to treat diabetes, some have been specifically approved for weight loss:
- Wegovy (semaglutide): Approved for chronic weight management in people with a BMI of 30 or higher, or 27 with a weight-related condition.
- Saxenda (liraglutide): Approved for weight management in similar patient groups.
In clinical trials, patients using these medications have lost an average of 10-15% of their body weight, making them highly effective for weight loss.
Learn more about how this medications support weight loss at Zappy Health’s blog on weight management.
Cardiovascular Health
Beyond blood sugar control and weight loss, GLP-1 has also been linked to cardiovascular health. Several studies have shown that GLP-1 receptor agonists can reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes, such as heart attack and stroke.
a) Mechanism of Cardiovascular Benefits
GLP-1 receptor agonists are thought to improve cardiovascular health through multiple pathways, including:
- Reducing Inflammation: It can help reduce inflammation in blood vessels, improving their function.
- Lowering Blood Pressure: Some studies have shown that this medications can help lower blood pressure, further supporting heart health.
For detailed clinical data on GLP-1 and cardiovascular benefits, see this study from the American Diabetes Association.
Common GLP-1 Medications and Their Uses
GLP-1 receptor agonists have become a cornerstone of treatment for type 2 diabetes and weight loss. Here’s a closer look at some of the most commonly prescribed medications:
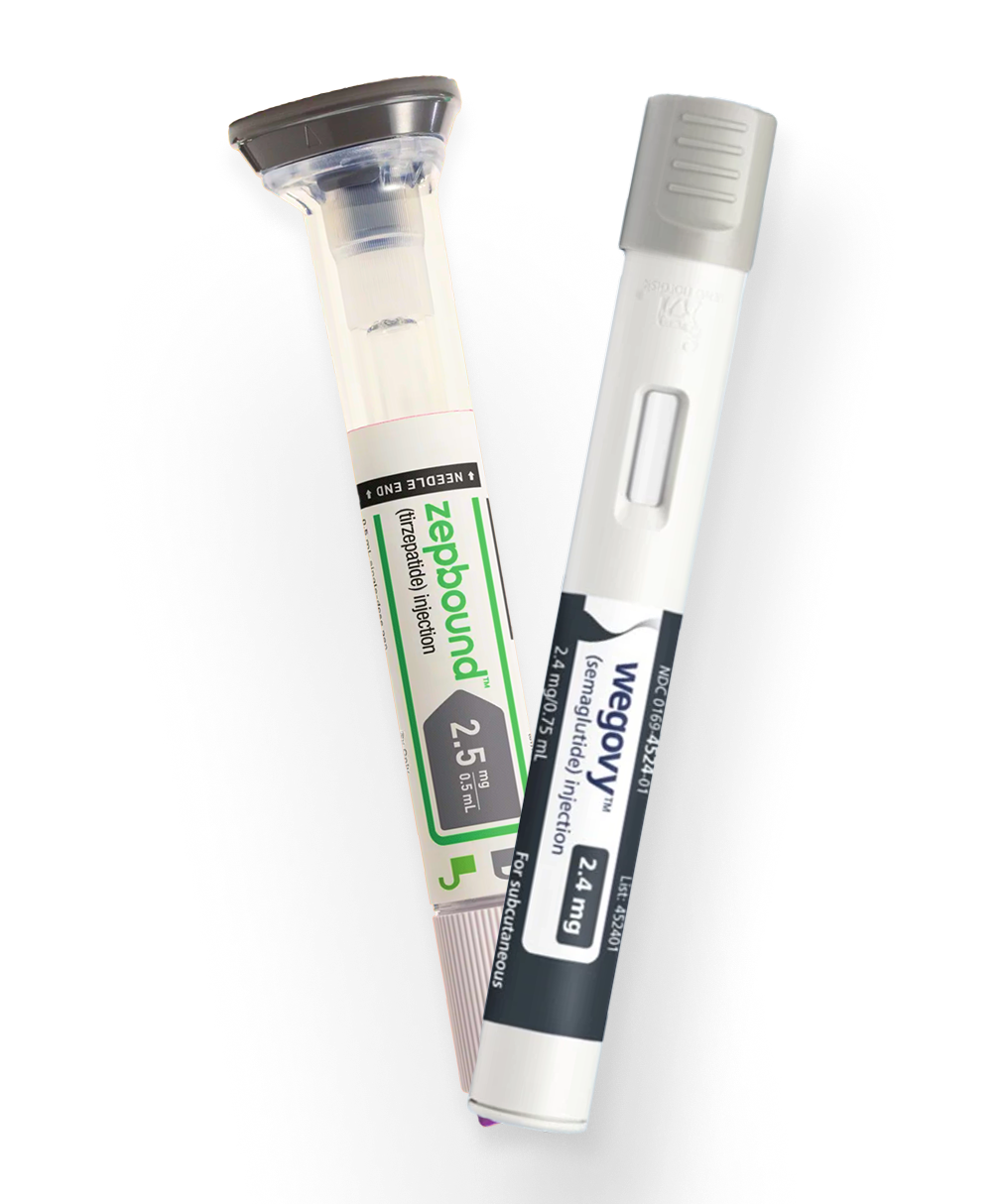
a) Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy)
- Uses: Type 2 diabetes (Ozempic), weight loss (Wegovy)
- Dosing: Administered as a weekly injection, starting at a low dose and gradually increasing.
- Effectiveness: Semaglutide is highly effective at lowering HbA1c and promoting weight loss.
b) Liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda)
- Uses: Type 2 diabetes (Victoza), weight loss (Saxenda)
- Dosing: Administered as a daily injection.
- Effectiveness: Liraglutide has been shown to reduce body weight and improve blood sugar control.
c) Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
- Uses: Type 2 diabetes
- Dosing: Weekly injection.
- Effectiveness: Effective for lowering blood sugar and providing cardiovascular benefits.
Are There Side Effects?
Like any medication, GLP-1 receptor agonists come with potential side effects. While many patients tolerate these medications well, others may experience:
a) Common Side Effects
- Nausea: The most commonly reported side effect, especially when starting treatment.
- Vomiting and Diarrhea: Often occur alongside nausea as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Decreased Appetite: While beneficial for weight loss, this can be uncomfortable for some.
b) Less Common Side Effects
- Hypoglycemia: Risk increases when GLP-1 is used alongside other diabetes medications like insulin.
- Pancreatitis: A rare but serious side effect that requires immediate medical attention.
To manage these side effects, healthcare providers may adjust the dosage or recommend taking the medication with food. If you experience any severe symptoms, consult your doctor immediately.
For a more in-depth look at potential side effects, visit WebMD’s guide on GLP-1 medications.
Who Should Use GLP-1 Medications?
Typically prescribed for:
- Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: To improve blood sugar control and reduce A1C levels.
- Individuals with Obesity or Overweight: To aid in weight loss when combined with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
- Those with a History of Cardiovascular Disease: To reduce the risk of heart-related complications.
It’s essential to discuss with your healthcare provider whether GLP-1 medications are right for you, especially if you have any pre-existing conditions or concerns. While this medications can offer significant benefits, they may not be suitable for everyone, such as individuals with a history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures that you receive a personalized treatment plan tailored to your unique needs.
How to Get Started with GLP-1 Medications
If you and your healthcare provider decide that a GLP-1 receptor agonist is right for you, here’s how you can get started:
a) Consult with a Healthcare Provider
Your first step will be a consultation with a doctor who can assess your overall health, weight loss goals, and current blood sugar control. They will recommend the most appropriate GLP-1 medication based on your needs.
b) Prescription and Dosing
Once a GLP-1 medication is prescribed, you’ll receive instructions on how to start. The medication often begins at a low dose to help your body adjust, with gradual increases over time to reach the maintenance dose. The dosing schedule varies depending on the medication—some are daily (like liraglutide), while others are weekly (such as semaglutide and dulaglutide).
c) Monitoring and Follow-Up
After starting, your healthcare provider will likely schedule follow-up visits to monitor your blood sugar levels, weight, and any side effects. These visits ensure that your medication is working as intended and allows for any necessary adjustments.
d) Long-Term Use and Lifestyle Changes
GLP-1 medications are most effective when combined with lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular exercise. These changes not only enhance the medication’s effects but also support long-term health and weight maintenance.
For tips on maximizing the benefits of your medication, check out Zappy Health’s guide to healthy living with GLP-1s.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can GLP-1 medications cure diabetes?
No, it cannot cure diabetes. They are highly effective at managing type 2 diabetes and controlling blood sugar levels, but they do not cure the underlying condition. Consistent use alongside lifestyle changes can, however, lead to significant improvements in health.
Q2: How long does it take to see results?
Most patients begin to see improvements in blood sugar control within the first few weeks. Weight loss results may take a few months, with significant changes typically occurring around the 3 to 6-month mark.
Q3: Are there any dietary restrictions?
While there are no strict dietary restrictions, eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods can enhance the effectiveness of GLP-1 medications. Avoiding high-fat, fried, and sugary foods can also help reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
Q4: Can I use GLP-1 medications if I’m pregnant?
It’s not recommended for use during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
For more FAQs and in-depth answers, visit Zappy Health’s GLP-1 FAQ page.
The Future of GLP-1 Medications
The success of this medications in diabetes management and weight loss has spurred further research into new treatments and combinations. Some areas of exploration include dual and triple agonists, like tirzepatide, which combine GLP-1 with other incretin hormones to potentially offer even greater benefits.
As research continues, it’s likely that new therapies will become available, offering more options for patients looking to manage their health. The future looks promising for individuals seeking effective, non-invasive treatment options for chronic conditions like diabetes and obesity.
Conclusion:
GLP-1 receptor agonists have revolutionized the way we approach type 2 diabetes and weight management. In addition to helping with blood sugar control and weight loss, they offer powerful GLP 1 cardiovascular benefits, making them a comprehensive solution for individuals with metabolic and heart health concerns. However, as with any medication, the key to success is finding the right treatment plan tailored to your unique needs.
If you’re considering a GLP-1 medication, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your options and determine the best path forward. With the right guidance and a commitment to your health, it could be the key to a healthier, more balanced life.
For more resources and to explore the best GLP-1 treatment options, visit Zappy Health’s comprehensive GLP-1 guide.