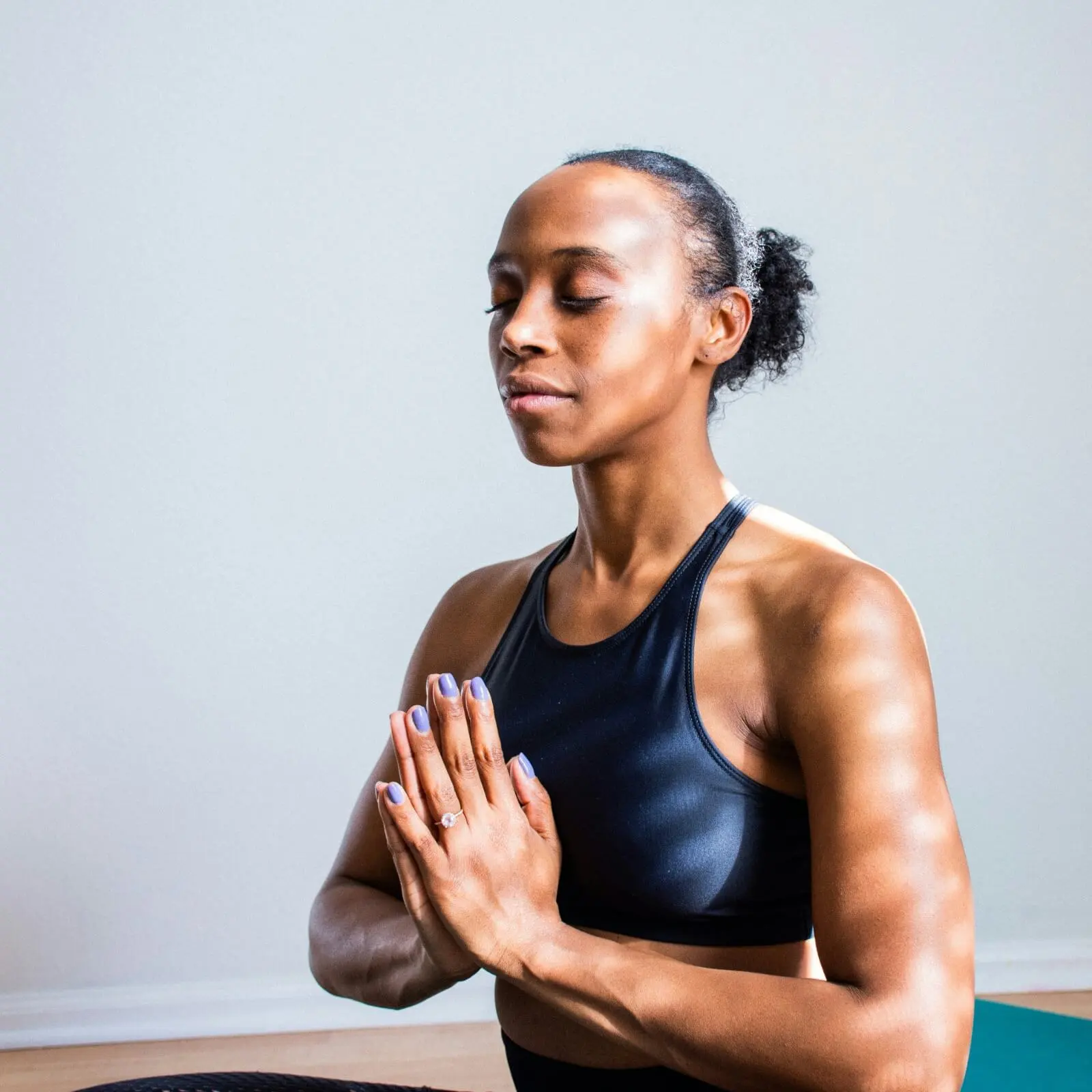
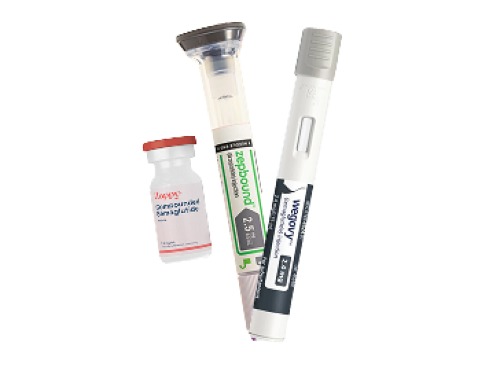
- Weight Loss
-
-
-
-
-
-
GET STARTED
-
-
-
-
- Anti-aging
-
-
-
-
DISCOVER
-
RESOURCES
-
-
-
-
-
-
GET STARTED
-
-
-
-
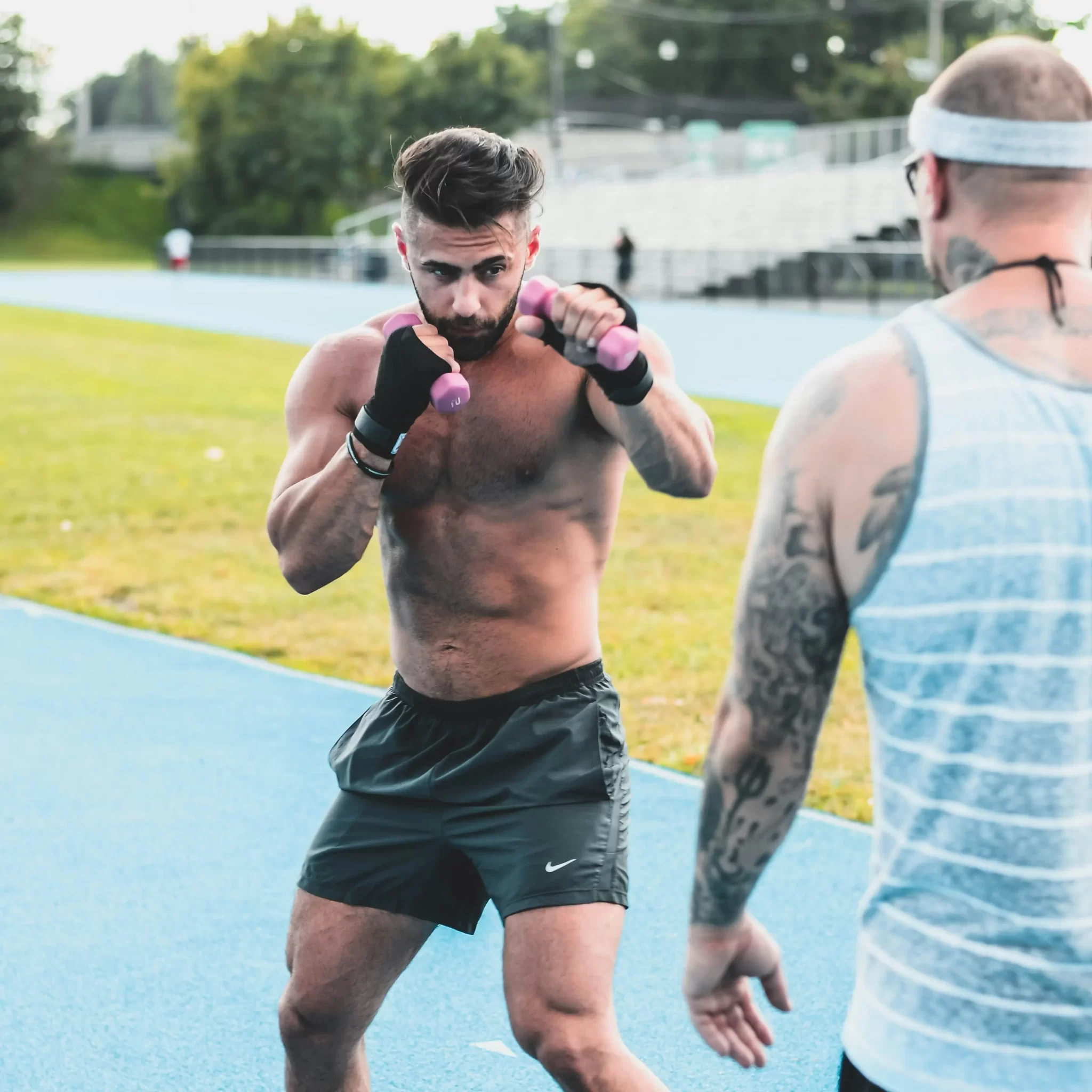
- Strength & Recovery
-
-
-
-
DISCOVER
-
Resources
-
-
-
-
-
-
GET STARTED
-
-
-
-
- Better Skin
-
-
-
-
Coming Soon
-
-
-
-
-
GET STARTED
Personalized Skin Care Regimen

-
-
-
-
- Blog
- Helpdesk